Quality controller – salary, responsibilities, and job requirements
Table of contents
The role of a quality controller is increasingly valued, with its importance growing across various industries. Discover what this job entails, what the requirements are, and how much you can earn in this position.
What does the job of a quality controller look like?
The work of a quality controller involves ensuring that products or services meet set quality standards and requirements. The person in this role is responsible for thoroughly examining and assessing each stage of production or service to detect and identify any defects. Quality controllers can work in various sectors—from the food industry to electronics and automotive. Their primary goal is to minimize the risk of delivering products that may not meet customer expectations or could pose health and safety hazards.
The daily responsibilities of a quality controller vary depending on the industry, but the job typically involves inspecting raw materials, overseeing production, and monitoring technological processes. If issues are identified, the quality controller collaborates with the production team to resolve them quickly. This role requires both analytical skills and strong communication, especially when explaining technical issues to other team members.
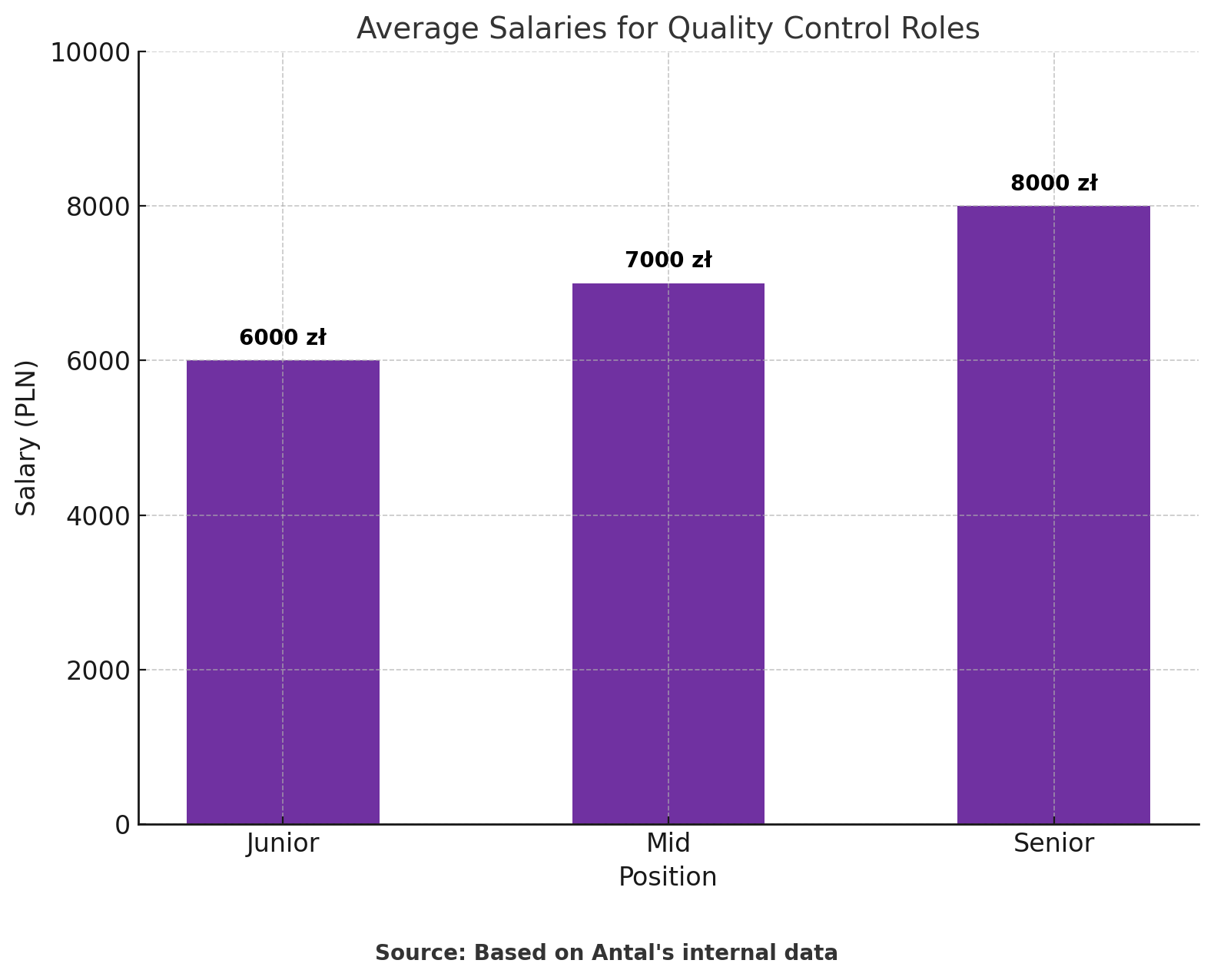
Earnings for the position of quality controller depend on the level of the position, the specific industry and the region. The average monthly salary for a junior specialist is PLN 6000, for a specialist PLN 7000 and for a senior specialist PLN 8000. Below is a chart with averaged salary values for selected positions:
Quality controller course – why is it worth it?
Courses for quality controllers are becoming increasingly popular and can significantly improve employment prospects in this field. Specialized training provides essential knowledge about quality standards, quality management systems, and methods for testing products and materials. Courses usually include both theoretical and practical sessions, equipping participants with the necessary skills. Notably, many companies prefer candidates who have completed certified training, especially in industries with high-quality standards.
When choosing a course, it’s advisable to review the program and verify if it covers topics relevant to a specific industry. A good course prepares individuals for the job by covering topics such as interpreting quality standards (e.g., ISO 9001), statistical methods used in quality control, and auditing techniques. Earning a certificate not only makes job hunting easier but can also increase salary and accelerate career progression in quality control.
Quality controller’s duties and requirements
The duties of a quality controller may vary depending on the specific company and industry, but the most common include:
- Conducting quality inspections of raw materials and products – Quality controllers check each stage of production, from raw materials to finished products, to ensure they meet quality standards.
- Documenting results – Maintaining records that document control results and identified irregularities. Clear documentation enables quick problem identification and subsequent analysis.
- Analyzing the causes of errors – When a defective product is found, the quality controller’s job is to analyze the root cause, helping prevent similar situations in the future.
- Collaborating with the production department – Quality controllers must communicate effectively with the production team to address any irregularities quickly.
- Familiarity with standards and regulations – Quality controllers must know and apply quality standards relevant to their industry, such as ISO 9001 or HACCP.
Job requirements for a quality controller vary by industry, but typically include:
- Technical education at the secondary or university level – Preferred fields include engineering, quality management, or production.
- Work experience – Many companies require candidates to have experience in a similar role or knowledge of the industry.
- Certificates and training – Courses and certifications in quality management can be an additional advantage and increase job prospects.
- Analytical and communication skills – The quality controller role demands precision and the ability to analyze control results.
- Familiarity with quality management software – Companies increasingly use software to support quality control processes, so proficiency in these tools is highly valued.
The quality controller profession is an attractive option for individuals who value precision and a commitment to excellence. With proper training, knowledge, and experience, one can expect a stable and well-paying job in companies dedicated to high production standards.