Process Automation Specialist – What Does the Role Involve?
Table of contents
An increasing number of companies are seeking ways to streamline their operations, and one of the most effective directions is process automation. It enables organizations to operate faster, more precisely, and more cost-effectively. Who is behind these transformations? The Process Automation Specialist – a professional who combines technical expertise with the ability to understand complex business structures.
What does their daily work entail, and how can you start a career in this field?
Process Automation Specialist – What Does the Role Involve?
An increasing number of companies are seeking ways to streamline their operations, and one of the most effective directions is process automation. It enables organizations to operate faster, more precisely, and more cost-effectively. Who is behind these transformations? The Process Automation Specialist – a professional who combines technical expertise with the ability to understand complex business structures. What does their daily work entail, and how can you start a career in this field?
Automation as a Response to Modern Business Challenges
Pressure to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and meet growing customer expectations drives companies to seek solutions that provide a competitive edge. Business process automation – both internal and customer-facing – is becoming increasingly critical year by year.
It’s no longer limited to large corporations – small and medium-sized enterprises are also investing in automation, recognizing its potential to reduce errors, shorten task execution time, and enhance service quality. This trend is part of a broader digital transformation, where data, technology, and speed become key to building market advantage.
Companies across various industries are implementing tools such as RPA (Robotic Process Automation), VBA macros, Power Automate, and Python scripts to automatically process data, populate forms, generate reports, or update systems. The growing importance of automation translates into an increasing demand for professionals who can implement and develop these solutions.
What Does a Process Automation Specialist Do?
A Process Automation Specialist is responsible for analyzing, designing, and implementing solutions that streamline the company's day-to-day operations. This person has the ability to “x-ray” business processes, identify areas for automation, and then design tools or scripts that take over repetitive tasks.
Their work doesn’t end with implementation. The specialist also monitors, tests, optimizes, and develops automation solutions to ensure they truly deliver value to the business and its employees. This role requires technical knowledge as well as the ability to collaborate with non-IT teams such as finance, HR, or sales.
Strong communication skills are essential – the specialist must understand end-user needs, translate them into technical specifications, and deliver functional and intuitive solutions.
Automation can be applied in a wide range of areas:
- Finance: invoice posting, report generation, payment tracking
- HR: contract generation, onboarding, employee data updates
- Sales: automated reporting, CRM updates, offer generation
- Customer Service: automatic email responses, service ticket management
Required Qualifications for a Process Automation Specialist
You don’t need to be a seasoned programmer to enter the field of automation. While education in computer science or automation can be an advantage, many companies are open to candidates with degrees in management, economics, or even social sciences – as long as they possess hands-on skills. Experience in process analysis and optimization or participation in automation projects is a strong asset.
Commonly required qualifications include:
- Familiarity with automation tools such as Power Automate, UiPath, Blue Prism, or Low-Code/No-Code platforms
- Ability to create VBA macros and work with advanced Excel features
- Basic knowledge of scripting languages such as Python, JavaScript, or VBA
- Process analysis and mapping (e.g., BPMN)
- Project work experience and technical documentation creation
- English proficiency for reading technical documentation and communicating in international environments
- Strong communication and collaboration skills
Additional advantages may include:
- Knowledge of Lean methodology
- Experience working with SAP
I Don’t Have a Technical Degree – How Can I Gain Practical Skills?
Many professionals – including those at the beginning of their careers – develop their competencies through online courses, industry certifications (such as UiPath RPA Developer), and by participating in automation projects within their current organizations, even on a small scale. Hackathons and internal innovation programs are also gaining popularity, offering opportunities to test new ideas and deploy them in real business settings.
What Are the Responsibilities of a Process Automation Specialist?
The scope of responsibilities may vary depending on the company and the maturity of its processes but typically includes:
- Analyzing and modeling business processes to identify opportunities for optimization and automation
- Designing automation solutions tailored to the company’s needs
- Implementing tools such as scripts, bots, or workflows
- Testing, deploying, and maintaining solutions using Low-Code/No-Code platforms and RPA tools
- Preparing technical documentation and reporting results
- Providing training and operational support to users
- Collaborating with business stakeholders and IT teams to gather requirements
In many companies, the Process Automation Specialist also acts as an advisor – participating in project meetings, helping define process goals, and proposing new solutions to improve daily operations.
This role may evolve over time – experienced professionals often advance to team leadership roles, solution architecture, or consulting positions supporting company-wide digital transformation.
What Salary Can You Expect as a Process Automation Specialist?
Salaries in this field are highly competitive – especially considering the dual business and technical nature of the role and the growing demand in both global and local markets.
According to the Antal 2024 Salary Report, monthly gross salaries are as follows:
- Junior Specialist: 10,000 – 14,000 PLN
- Mid Specialist: 16,000 – 24,000 PLN
- Senior Specialist: 25,000 – 32,000 PLN
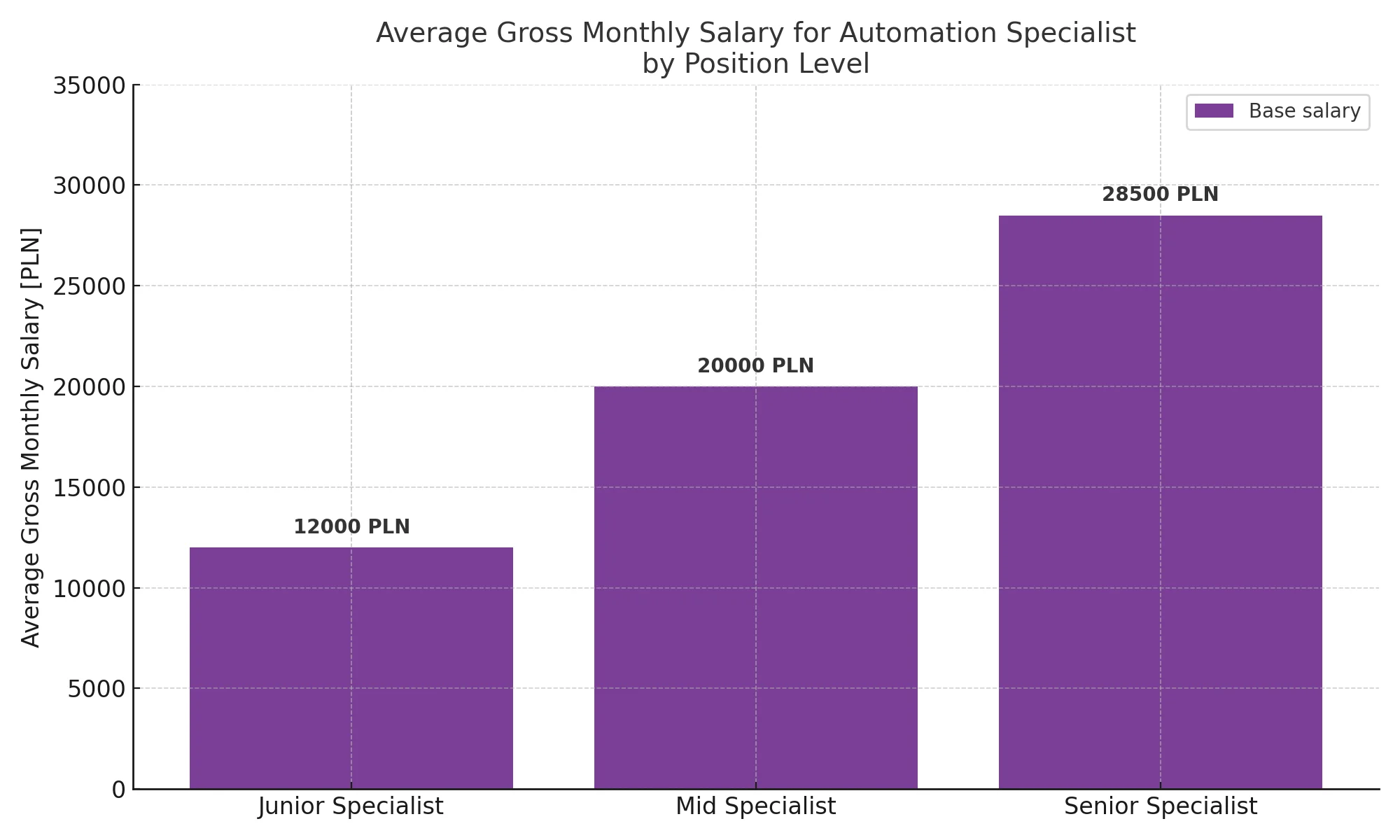
Compensation depends on experience, project types, proficiency in specific technologies, and the form of employment (permanent contract vs. B2B). In the case of B2B contracts, rates can be even higher – especially for specialists involved in complex implementations at large organizations.
Does Location Matter?
Absolutely. Professionals based in major cities or working remotely for international clients can expect more attractive compensation packages. In metropolitan areas such as Warsaw, Wrocław, Kraków, or Gdańsk, there are more job offers, and the competition for talent drives employers to offer better salaries, flexible working arrangements, and additional benefits such as training, medical packages, or certification support.
Remote work, on the other hand, opens up opportunities for participating in international projects without the need to relocate. Companies from the US, Germany, the UK, or Scandinavia are increasingly hiring Polish experts, appreciating their skills and dedication. In such cases, salaries may be offered in euros or dollars, making this path financially appealing. More and more professionals choose hybrid or fully remote models, combining flexibility with international career growth.
Is This a Profession of the Future?
Undoubtedly, yes. The growing role of automation in business, focus on efficiency, and the rising popularity of no-code and low-code tools mean that skills in this area will become even more valued. Moreover, the role of Process Automation Specialist offers vast development potential – from technical paths (e.g., RPA Architect, Developer) to project management or business analysis.
This is an ideal career for those who enjoy combining analytical thinking with technology and want to make a real impact on process improvement and work quality in organizations. It is also a profession resistant to automation – because it's the Automation Specialists who will be designing the future of work.